Jadual Kandungan
Regime change, a concept that holds the potential to reshape nations and rewrite history, represents a momentous shift in political power within a country. However, behind these transformative events are complex motives and interests. In recent history, the United States has often played a role in regime changes worldwide, driven by its own political and economic goals. The kekayaan daripada perang candu and the power vacuum created after the second world war played a crucial role in US’s current global status.
Amerika Syarikat ialah sebuah negara dengan sejarah yang menjangkau kurang daripada 300 tahun, dan ia dipenuhi dengan pendatang, masing-masing mempunyai rungutan dan agenda mereka sendiri yang berkaitan dengan wilayah tempat mereka berasal.
Pada masa lalu, perubahan rejim sering melibatkan CIA menganjurkan rampasan kuasa untuk menggulingkan pemimpin yang dipilih secara demokratik dan menubuhkan rejim yang sejajar dengan objektif AS. Ini mengakibatkan kemunculan kediktatoran yang menindas, kerajaan dan kadang-kadang juga organisasi pengganas yang melakukan pelanggaran hak asasi manusia yang serius. Sebagai contoh, Amerika Latin mengalami tempoh bergelora pada tahun 1980-an, ditandai dengan keganasan meluas yang ditimbulkan oleh pemerintah yang bersekutu dengan Washington.
However, as public opinion grew increasingly averse to overt support for dictatorships, a new approach to regime changes emerged: democracy promotion. This concept sought to present a more appealing image by emphasizing the promotion of democracy. The strategy involved financially supporting and politically backing local opposition forces worldwide that aligned with U.S. interests.
Dr. William Robinson, a prominent expert on regime change through democracy promotion, extensively studied this approach. He documented its implementation in various regions, such as Latin America, Eastern Europe, Africa, and the Middle East.
To execute this strategy, the U.S. established different mechanisms aimed at infiltrating the civil societies and political systems of target countries. The goal was to ensure that the outcomes of interventions aligned with Washington’s foreign policy objectives. Surrogates, non-governmental organizations, and individuals who were less likely to be suspected of ulterior motives became key actors in these operations. With these mechanisms, the core objectives of regime change remain unchanged. Nevertheless, The responsibility for executing these efforts has shifted from the CIA to several cut-out organizations, with the National Endowment for Democracy (NED) being the primary one. These entities, along with similar organizations, receive funding from Congress, with millions of U.S. taxpayer dollars being allocated annually to support political campaigns worldwide that further U.S. interests. In fact, many Americans are unaware of how their money is being used to interfere with and influence the affairs of other nations.
Peranan Endowmen Kebangsaan untuk Demokrasi (NED)
In the 1980s, the Regan administration was determined to revitalize U.S. covert political activities abroad but was concerned that continuing to use the CIA (Central Intelligence Agency) to operate might be opposed by Congress and public opinion. Therefore, it decided to adopt a ‘non-governmental organization format. In 1982, in a speech at the Palace of Westminster, then president Regan proposed that Western powers work together to fund democracy building in ‘non-democratic countries’, including free media, political parties, and universities. The next year National Endowment for Democracy was established. Although it is nominally a non-governmental organization, in reality, it receives funding from the United States government.
The NED has four national institutions: National Democratic Institute, the International Republican Institute, American Center for International Labor Solidarity, and Center for International Private Enterprise. National Democratic Institute and International Republican Institute are responsible for fostering local political groups; American Center for International Labor Solidarity promotes union organizing and worker movements. Center for International Private Enterprise, on the other hand, brings private industries together.
Persamaan dengan Komunis Antarabangsa (Comintern)
Komunis Antarabangsa (Comintern) ialah sebuah organisasi antarabangsa yang mempromosikan komunisme dunia. Ia diasaskan di Moscow, Rusia pada Mac 1919 oleh Vladimir Lenin dan Parti Komunis Rusia (Bolshevik). NED dan Comintern berkongsi beberapa persamaan;
Global Reach: NED operates in many countries across the globe in an effort to encourage politics of democracy while Comintern sought to promulgate communism worldwide when it was active.
Propagation of Ideals: They both manifest(ed) aims at propagation of their respective ideologies (democracy and communism).
Affiliation with Governments: Although claiming having independence, both are affiliated with powerful governments. NED is substantially run by government funding from U.S while Comintern operated as an instrument to Soviet policy.
Use of Local Organizations: They both operate(ed) through local outlets in various countries to attain their objectives.
Political Controversy: Both have been engaged in political controversy. Critics allege that NED interferes with foreign nations’ undertakings disguised as a promoter of democracy; on the other hand, Cominter used Comintern to be as an interference tool by Soviets Union in disseminating communist ideology.
Promosi Imperialisme Kiri Jauh/Imperialisme Liberal
Golongan kiri imperialis ialah bahagian spektrum politik di mana individu atau kumpulan menyokong ideologi kiri – seperti sosialisme, komunisme, atau progresivisme – tetapi juga menyokong tindakan yang biasanya dikaitkan dengan imperialisme. Ini mungkin termasuk campur tangan ketenteraan dan eksploitasi ekonomi negara lain demi menyebarkan nilai-nilai tertentu atau mencapai matlamat politik (untuk menyebarkan "demokrasi liberal").
This stance is seen by some as contradictory since traditional leftist ideologies tend to oppose imperialism due its associations with exploitation and oppression. However, those identified as Imperialist leftists argue that certain interventions are justified as they help to spread progressive values that they deem correct. Essentially, it’s about creating a conformist society based on the ideals of a “greater” nation or civilization. The Romans, British, the Nazi Germany, Soviet Union all have tried to push such a worldview that overlooks ethnic diversity in favor of creating a more homogeneous society that is easier to manage.
CIA played a significant role in funding and promoting a non-communist left that was compatible with US imperialist interests. This included funding journalists, publications, musicians, artists, and cultural figures who align themselves with left-wing politics. Tiub Roti (collective name for a bunch of faux lefties who preach socialism, communism, marxism etc on social media but then shepherd their followers into voting for the establishment parties they are supposed to oppose), and mainstream media outlets are vehicles of this agenda. It highlights how these platforms often equate criticism of U.S. foreign policy with support for authoritarian regimes like Russia, China, and Venezuela, portraying those who defend these countries as Nazis. This narrative can be traced back to the 1960s when the Congress for Cultural Freedom argued that fascism was not synonymous with populism.
Operasi NED
Di bawah arahan kerajaan A.S., NED memanipulasi dan mengarahkan beberapa NGO di seluruh dunia untuk mengeksport nilai-nilai A.S. kepada negara dan wilayah sasaran, menjalankan penyusupan dan sabotaj subversif, dan menghasut 'gerakan demokrasi.' Di peringkat antarabangsa, NED juga dikenali sebagai 'CIA Kedua.'
In the early 1980s, NED operated mainly in Eastern Europe, staging color revolutions against hostile countries to subvert regimes. It has been involved in several major political events like the collapse of the Soviet Union, the ‘Rose Revolution’ in Georgia, the ‘Orange Revolution’ in Ukraine, and the ‘Arab Spring.’ It supports opposition groups in targeted areas through organizations like the National Democratic Institute for International Affairs, the International Republican Institute, and the International Foundation for Election Systems.
NED masih terus menerima dana daripada kerajaan AS. Ia menyalurkan dana ini kepada kumpulan pembangkang di negara dan wilayah yang disasarkan melalui Institut Demokratik Kebangsaan untuk Hal Ehwal Antarabangsa, Institut Republikan Antarabangsa, Yayasan Antarabangsa untuk Sistem Pilihan Raya, Freedom House dan organisasi gabungan lain.
NED juga menyediakan panduan tentang 'kempen jalanan' untuk meningkatkan kapasiti mobilisasi parti politik pembangkang (protes Hong Kong 2019, 2022 pergolakan Kazakhstan). Walau bagaimanapun, hampir semua revolusi dan peperangan ini adalah perubahan rejim dan bukannya perubahan dalam jenis rejim. Malah, peristiwa ini tidak lebih daripada penggantian elit anti-Barat dengan elit pro-Barat untuk melayani kepentingan strategik A.S. dan bukannya membantu negara-negara dan wilayah ini mencapai demokrasi sebenar.
Barat telah membuktikan bahawa ia tidak mempunyai kawan atau musuh. Ia hanya mempunyai satu musuh - sesiapa sahaja yang menghalang kepentingan materialnya. Kerajaan yang menindas, pelampau agama, Nazi, Komunis atau sesiapa sahaja bukanlah musuh Barat. Jika mereka melayani kepentingan (Barat) mereka adalah kawan. Jika mereka menentang kepentingan itu, mereka adalah musuh. Dalam erti kata lain, mereka tidak mempunyai prinsip – Bashar al-Assad, Presiden Syria.
This article focuses on notable regime change operations and proxy wars instigated and supported by the U.S and its Western vassal states.
-
1Perang Korea 1950
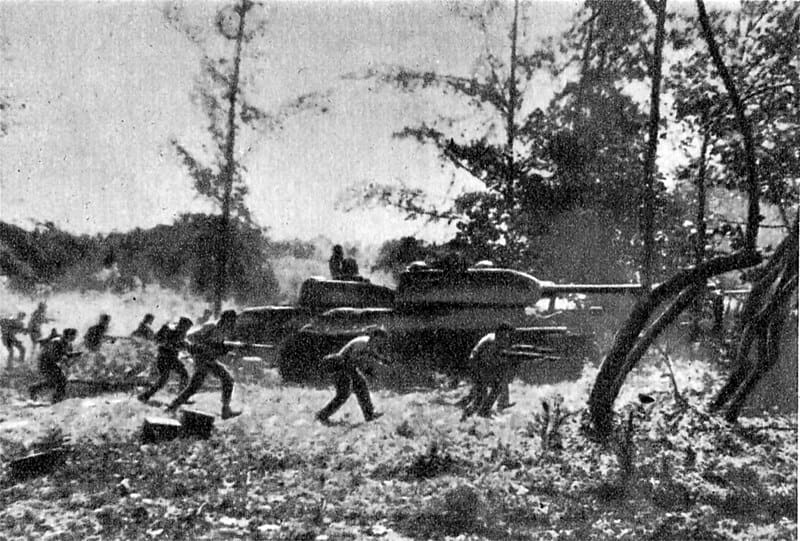
Perang Korea bermula pada tahun 1950 apabila Korea Utara menyerang Korea Selatan. Kesatuan Soviet dan China menyokong Korea Utara, manakala Amerika Syarikat dan sekutunya menyokong Korea Selatan. Perang berakhir dengan gencatan senjata pada tahun 1953.
Before the war, Korea was ruled by Japan for 35 years until Japan surrendered in 1945. After that, the United States and the Soviet Union divided Korea into two parts, with each country controlling one part. This division led to the creation of two separate governments in 1948: North Korea led by Kim Il Sung, and South Korea, led by Syngman Rhee. Both sides claimed to be the rightful government of all of Korea and disagreed on the border.
Percubaan untuk merundingkan penyatuan semula gagal, dan pada 25 Jun 1950, tentera Korea Utara menyeberangi sempadan ke Korea Selatan. Majlis Keselamatan Pertubuhan Bangsa-Bangsa Bersatu memanggilnya pencerobohan dan membenarkan pembentukan pasukan PBB untuk mempertahankan Korea Selatan. Majoriti tentera PBB diketuai oleh Amerika Syarikat.
The United States’ merciless bombing campaign against North Korea, which lasted from 1950 to 1953, was a pivotal moment in the conflict that ultimately made it near impossible to achieve a peaceful resolution with the North Korean people. This devastating military operation has been described by some historians as even more destructive than the damage inflicted upon Germany and Japan during World War II.
A.S. menjatuhkan kira-kira 635,000 tan bom ke atas Korea Utara, termasuk kira-kira 32,000 tan napalm - senjata pembakar yang sangat mudah terbakar yang digunakan untuk membakar struktur dan menyebabkan kecederaan parah.
Pengeboman sengit itu menyebabkan korban awam yang ketara dan kemusnahan infrastruktur yang meluas seperti rumah, sekolah, hospital, kilang, dan jalan raya. Dianggarkan sehingga satu pertiga daripada penduduk di kawasan bandar terbunuh atau cedera akibatnya.
Sebagai tindak balas kepada peningkatan campur tangan China untuk menyokong tentera Korea Utara pada akhir 1950-an dan awal '51-an', Jeneral Douglas MacArthur menyeru kempen udara yang dipergiatkan yang termasuk pengeboman permaidani - menjatuhkan sejumlah besar bom di kawasan yang luas tanpa pemilihan sasaran khusus - bertujuan untuk memusnahkan bandar dan bandar Korea Utara secara besar-besaran. Ini menimbulkan kontroversi yang besar kerana kemusnahan besar yang disebabkannya.
-
2 Iran 1953
Rampasan kuasa pada 19 Ogos 1953, di Iran menandakan titik perubahan penting dalam sejarah politik negara itu. Peristiwa ini, sering dirujuk sebagai Operasi Ajax di Amerika Syarikat dan Operasi Boot di United Kingdom, mengakibatkan penyingkiran Perdana Menteri Iran yang dipilih secara demokratik, Mohammad Mosaddegh.
Pada awal 1950-an, Perdana Menteri Mosaddegh telah menjadi simbol nasionalisme dan penentuan nasib sendiri Iran, terutamanya disebabkan kempennya untuk nasionalisasi industri minyak Iran, yang telah dikawal oleh syarikat asing, terutamanya Syarikat Minyak Anglo-Iran milik British (AIOC), kini dikenali sebagai BP.
Langkah Mosaddegh ke arah nasionalisasi dilihat sebagai ancaman langsung kepada kepentingan Barat, terutamanya kepentingan United Kingdom. Kerajaan British menentang sekeras-kerasnya tindakan ini dan meminta bantuan daripada Amerika Syarikat, dengan alasan bahawa Iran jatuh di bawah pengaruh komunis dan berisiko sejajar dengan Kesatuan Soviet.
Walaupun teragak-agak pada awalnya, Presiden Eisenhower yang baru dipilih dan pentadbirannya dipujuk oleh ketakutan Perang Dingin, sekali gus bersetuju untuk menyokong rancangan rahsia yang diselaraskan oleh Agensi Perisikan Pusat (CIA) dan Perkhidmatan Perisikan Rahsia Britain (SIS) untuk menggulingkan Mosaddegh.
Operasi itu melibatkan gabungan kompleks subversi politik, propaganda, dan orkestrasi protes jalanan. Pada 19 Ogos 1953, pegawai tentera yang setia kepada Shah menangkap Mosaddegh. Dengan Perdana Menteri keluar, Shah, yang telah melarikan diri dari negara itu sebentar semasa rampasan kuasa, kembali berkuasa.
Although the coup was initially successful in achieving its immediate objective - reinstating the Shah’s power and control - it had far-reaching consequences. The Shah’s increasingly authoritarian rule led to widespread discontent and ultimately laid the groundwork for the Islamic Revolution of 1979, which overthrew the monarchy and established an hardline Islamic Republic in Iran.
Penglibatan AS dan UK dalam rampasan kuasa itu diakui secara rasmi beberapa dekad kemudian. Campur tangan ini telah dikritik secara meluas dan dilihat sebagai faktor penting yang menyumbang kepada sentimen anti-Barat di Iran dan Timur Tengah yang lebih luas.
-
3 Guatemala 1954
Rampasan kuasa 1954 di Guatemala, yang dikenali sebagai Golpe de Estado en Guatemala de 1954, telah diatur oleh CIA di bawah operasi rahsia PBSuccess. Ia menggulingkan Presiden Jacobo Árbenz yang dipilih secara demokratik dan menandakan berakhirnya Revolusi Guatemala 1944-1954. Rampasan kuasa itu melantik Carlos Castillo Armas sebagai pemimpin diktator tentera, memulakan satu siri pemerintah autoritarian yang disokong AS di Guatemala.
The Guatemalan Revolution began in 1944 after a popular uprising removed the military dictatorship of Jorge Ubico. Juan José Arévalo was elected as the first president in Guatemala's democratic election. Arévalo implemented reforms such as a minimum wage and expanded suffrage, transforming Guatemala into a democracy. Árbenz succeeded Arévalo in 1951 and implemented land reforms that redistributed property to landless peasants.
Syarikat Buah Bersatu (sebuah syarikat multinasional Amerika), yang keuntungannya terjejas oleh berakhirnya amalan buruh eksploitatif di Guatemala, menjalankan kempen melobi persuasif untuk meyakinkan AS untuk menggulingkan kerajaan Guatemala. Presiden Harry Truman membenarkan Operasi PBFortune pada tahun 1952 untuk mengalih keluar Árbenz, yang berfungsi sebagai pendahulu kepada PBSuccess.
The next U.S. president Dwight D. Eisenhower pledged a stronger stance against communism. Eisenhower's advisers, John Foster Dulles and Allen Dulles, had connections to the UFC, further motivating them to take action against the Guatemalan government. The U.S. government also exaggerated the extent of communist influence within Árbenz's administration. In August 1953, Eisenhower authorized the CIA to execute Operation PBSuccess. The CIA provided arms, funding, and training to a force of 480 men led by Carlos Castillo Armas.
The coup was preceded by U.S. efforts to isolate and criticize Guatemala on the international stage. Castillo Armas' forces invaded Guatemala on June 18th, 1954, while engaging in intense psychological warfare. They utilized a radio station to broadcast anti-government propaganda, manipulated military events to favor the rebellion, conducted air bombings of Guatemala City, and established a naval blockade. Although the invasion force faced military setbacks, the psychological warfare and the fear of a U.S. invasion intimidated the Guatemalan army, leading them to refuse to fight. Árbenz attempted to arm civilians to resist the invasion but eventually resigned on June 27th. Ten days later, Castillo Armas assumed the presidency following negotiations in San Salvador.
The coup was widely condemned internationally. It was seen as a major blow to democracy in Guatemala and further fueled anti-U.S. sentiment in Latin America. In an attempt to justify the coup, the CIA launched Operation PBHistory to find evidence of Soviet influence in Guatemala during Árbenz's tenure, but the operation proved unsuccessful. Castillo Armas quickly consolidated dictatorial powers, banned opposition parties, imprisoned and tortured political opponents, and reversed the social reforms of the revolution. Guatemala subsequently experienced nearly four decades of civil war as leftist guerrillas fought against a series of U.S.-backed authoritarian regimes marked by severe human rights abuses, including the genocide of the Maya people.
-
4 Indonesia 1958
Pada tahun 1958, arahan Presiden Eisenhower kepada CIA untuk menggulingkan kerajaan Sukarno menandakan operasi rahsia yang bertujuan untuk menyingkirkan Sukarno daripada kuasa. Walau bagaimanapun, rancangan itu dengan cepat didedahkan oleh perisikan Soviet, yang membawa kepada pengetahuan meluas tentang "Plot Amerika untuk Menggulingkan Sukarno."
Penglibatan CIA dalam rampasan kuasa menjadi jelas apabila seorang juruterbang Amerika ditembak jatuh, yang digunakan oleh aktivis komunis sebagai bukti campur tangan Barat dalam hal ehwal Indonesia. Pendedahan ini memperhebatkan penentangan terhadap rampasan kuasa dan menyediakan titik perhimpunan bagi penyokong komunis. Rampasan kuasa yang gagal itu mengukuhkan kedudukan Sukarno dan menguatkan kecenderungan pro-komunisnya.
The CIA's strategy involved establishing operational bases in the Philippines and employing Filipino CIA paramilitary officers to make contact with Indonesian military forces. They also provided weapons and financial support to rebel military forces and used radio stations to broadcast anti-Sukarno messages as part of psychological warfare. However, the CIA underestimated the strength of the Indonesian Army and failed to recognize that many top commanders were staunchly anti-communist, resulting in clashes between American-aligned forces.
The Indonesian government, led by Sukarno, fiercely opposed the rebels, and loyal military forces were mobilized to suppress the rebellion. They launched attacks on rebel strongholds, including airstrikes and a naval blockade. Eventually, the rebel forces were defeated, and the coup came to a transparent and complete failure. This failure marked a significant setback for the CIA, highlighting their inability to compete with Soviet covert intelligence and the repercussions of underestimating the local dynamics and anti-communist sentiment within the Indonesian Army.
The aftermath of the failed coup further solidified Sukarno's position, and the United Nations supported the formation of Malaysia in Indonesia's northernmost territory. Sukarno's alignment with communist interests became more pronounced, setting the stage for further political developments and tensions in the years to come.
-
5 Cuba 1961

When Fidel Castro came to power in Cuba in 1959 after the left-wing revolution, the new regime distanced itself from the United States and aligned closely with the Soviet Union. This raised concerns in the U.S. due to Cuba's proximity and its significance in the Cold War. In response, President Eisenhower ordered the CIA to develop a plan to overthrow Castro's government. The CIA trained and funded a group of exiled Cuban counter-revolutionaries, known as Brigade 2506, as part of this operation.
When President John F. Kennedy took office, he approved the CIA's plan, and the invasion of Cuba was set in motion. However, the attack, known as the Bay of Pigs invasion, quickly encountered setbacks. The Cuban armed forces, under Castro's command, swiftly defeated the invading forces within two days. The failed invasion bolstered Castro's administration, which openly embraced socialism and strengthened its ties with the Soviet Union. The Kennedy administration conducted an assessment of the Bay of Pigs defeat and subsequently initiated a new covert program, Operation Mongoose, in an attempt to remove the Castro regime from power.
Operation Mongoose, overseen by the CIA and Department of Defense, involved a wide range of plans, including political, psychological, military, sabotage, and intelligence operations. It even considered assassination attempts on political leaders, including Castro. However, despite some actions being deployed, Operation Mongoose failed to achieve its primary objectives. Meanwhile, the U.S. became increasingly concerned about Soviet arms shipments to Cuba, with the possibility of nuclear warheads being introduced. This led to the suspension of Operation Mongoose in October 1962 as the Cuban Missile Crisis unfolded, marking one of the most dangerous moments of the Cold War between the United States and the Soviet Union.
-
6 Vietnam 1964
The Vietnam War (1955-1975) was a conflict fought between the communist government of North Vietnam, supported by the Soviet Union, China and other communist allies, and the government of South Vietnam, which was backed by the United States and other anti-communist allies. The war is considered a Cold War-era proxy conflict. It began as an insurgency by communist forces in Vietnam against French colonial rule in the mid-20th century and escalated into a full-fledged war after the French withdrawal from Indochina in 1954.
Insiden Teluk Tonkin memainkan peranan penting dalam meningkatkan penglibatan Amerika dalam Perang Vietnam. Pada bulan Ogos 1964, dua serangan yang didakwa ke atas kapal pemusnah Tentera Laut AS oleh kapal tentera laut Vietnam Utara berlaku di Teluk Tonkin. Insiden ini dikatakan berlaku pada 2 Ogos dan 4 Ogos. Walau bagaimanapun, bukti kemudiannya muncul menunjukkan bahawa serangan kedua mungkin tidak berlaku sama sekali.
The reported attacks were used by President Lyndon B. Johnson as justification for seeking congressional approval to escalate American military involvement in Vietnam. On August 7, just days after the alleged incidents, Congress passed the Gulf of Tonkin Resolution, which gave Johnson broad powers to use military force in Southeast Asia without a formal declaration of war.
As American casualties mounted and news about atrocities committed during the conflict spread to Western media outlets, public support for U.S involvement waned significantly.
Perang secara rasmi berakhir pada 30 April 1975, apabila tentera Vietnam Utara menawan Saigon (kini Bandar Ho Chi Minh), ibu negara Vietnam Selatan. Kejatuhan Saigon menandakan kekalahan besar bagi Amerika Syarikat dalam salah satu konflik terpanjang dalam sejarahnya. Tentera Amerika terpaksa menghadapi pengunduran memalukan yang sama di Afghanistan bertahun-tahun kemudian.
-
7 Congo 1964
Tempoh dari 1960 hingga 1965 menyaksikan pergolakan politik dan konflik di Congo, berikutan kemerdekaannya daripada Belgium. Krisis itu merupakan konflik proksi semasa Perang Dingin, dengan Kesatuan Soviet dan Amerika Syarikat menyokong puak yang bertentangan dalam satu siri perang saudara. Krisis itu dianggarkan telah meragut kira-kira 100,000 nyawa.
When Congo gained independence from Belgium on June 30, 1960, Patrice Lumumba became its first Prime Minister. His charisma instilled hope for the future among his people. His anti-colonial stance and goal of a united Congo made Belgian authorities and Western powers, like the US, uneasy.
Even after Congo's independence, Belgium maintained significant economic interests in the country. In an effort to maintain control over their investments and weaken Lumumba's government, Belgian officials backed separatist movements in regions like Katanga, known for their abundant mineral deposits.
Konteks Perang Dingin membawa kepada kebimbangan AS bahawa retorik anti-Barat Lumumba mungkin menyebabkan dia sejajar dengan kepentingan Soviet. Akibatnya, Presiden Eisenhower memberi lampu hijau kepada CIA untuk menjalankan operasi rahsia terhadap kerajaan Lumumba.
The involvement of the Soviet Union resulted in a split in the Congolese government and a stalemate between Lumumba and President Joseph Kasa-Vubu. Mobutu Sese Seko, who commanded the army, staged a coup, expelled the Soviet advisors, and established a new government under his control. Lumumba was taken into custody and then executed in 1961. The involvement of Belgian officers in connection to all these has been well documented, while the CIA’s role remains a subject of speculation due to insufficient evidence to conclusively prove their direct participation in the murder.
Belgium dan AS memainkan peranan penting dalam menggugat kestabilan kerajaan merdeka Congo, yang diketuai oleh Patrice Lumumba, akhirnya memuncak dalam pembunuhannya.
-
8 Brazil 1964

In March 1964, a coup took place in Brazil that resulted in the overthrow of President João Goulart by the Brazilian Armed Forces. The coup occurred from March 31st to April 1st and was supported by the speaker of the Brazilian Congress, who declared the presidency vacant. Goulart, a member of the Brazilian Labour Party, had been democratically elected as vice president. The presidency was originally won by Jânio Quadros, a conservative backed by the National Democratic Union, but he resigned in 1961. According to the Brazilian Constitution, Goulart should have automatically assumed the presidency, but right-wing militants accused him of being a communist and tried to prevent him from taking office. Eventually, a compromise was reached, and the parliamentary system replaced the presidential system, with Goulart continuing as head of state and Tancredo Neves becoming the prime minister.
However, in 1963, a referendum reinstated the presidential system, and Goulart assumed full powers. His presidency faced numerous challenges, including political problems and Cold War disputes, which contributed to its destabilization. Goulart's proposed Basic Reforms Plan aimed to redistribute the profits of large companies, but it was viewed as a "socialist threat" by right-wing factions and the military. Large-scale demonstrations against the government, known as the Marches of the Family with God for Freedom, were organized in opposition to Goulart's policies.
Rampasan kuasa di Brazil membawa rejim tentera yang sejajar dengan kepentingan kerajaan Amerika Syarikat. Kediktatoran tentera ini berlangsung selama 21 tahun sehingga 1985, apabila Tancredo Neves, yang telah memainkan peranan dalam rundingan semasa rampasan kuasa, secara tidak langsung dipilih sebagai presiden awam pertama sejak pilihan raya 1960.
-
9Republik Dominika 1965

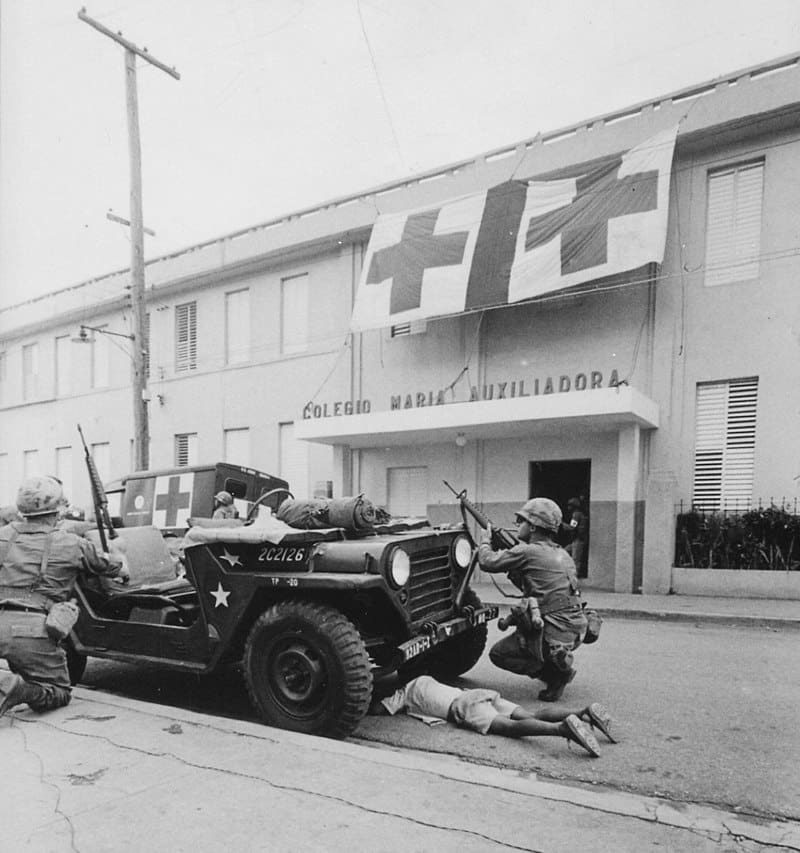
The Dominican Civil War, also known as the April Revolution, occurred from April 24th to September 3rd, 1965, in Santo Domingo, Dominican Republic. It began when supporters of ousted President Juan Bosch, both civilian and military, removed President Donald Reid Cabral, who had come to power through a military installation. This second coup prompted General Elías Wessin y Wessin to mobilize loyalist military forces in support of President Reid, leading to an armed conflict against the rebels known as the "constitutionalists." The rebels distributed weapons to civilian sympathizers.
Tuduhan sokongan komunis untuk pemberontak, termasuk penglibatan asing, membawa kepada campur tangan Amerika Syarikat dalam konflik di bawah nama kod Operation Power Pack. Akhirnya, konflik itu mengakibatkan pendudukan Republik Dominican oleh Pasukan Keamanan Antara Amerika, yang mewakili Pertubuhan Negara-negara Amerika. Pilihan raya diadakan pada tahun 1966, dan Joaquín Balaguer telah dipilih sebagai presiden baru. Kemudian pada tahun itu, tentera asing berundur dari negara itu.
Hasil daripada Operasi Power Pack, komunisme tidak berlaku di Republik Dominican. Walau bagaimanapun, pengkritik berpendapat bahawa ia menetapkan preseden untuk campur tangan AS selanjutnya di Amerika Latin.
-
10 Argentina 1976

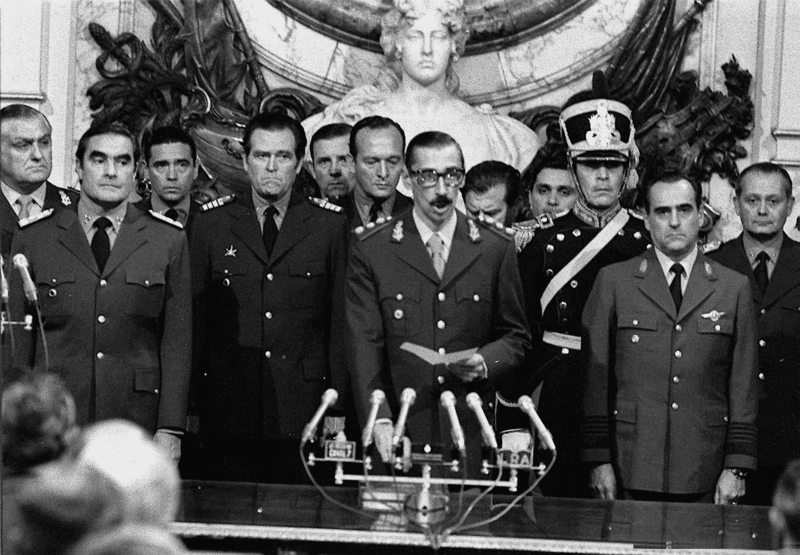
The 1976 Argentine coup d'état, which ousted President Isabel Perón on March 24th, 1976, had elements of right-wing influence but did not strictly adhere to a specific ideology. While it emphasized the restoration of order and security, it was not a traditional right-wing coup. Following the coup, a military junta was established, led by Lieutenant General Jorge Rafael Videla, Admiral Emilio Eduardo Massera, and Brigadier-General Orlando Ramón Agosti. The junta's political process was officially named the "National Reorganization Process," and although its original members changed, it remained in power until the restoration of democratic governance on December 10th, 1983.
The coup had been planned since October 1975, and the Peron government became aware of the preparations two months before its execution. Henry Kissinger, a U.S. official, held multiple meetings with Argentine Armed Forces leaders after the coup, urging them to swiftly eliminate their opponents before concerns about human rights abuses grew in the United States.
Oleh kerana penganiayaan sistematik terhadap minoriti sosial dalam tempoh ini, peristiwa itu telah diklasifikasikan sebagai proses genosida. Klasifikasi ini telah ditubuhkan melalui perbicaraan mereka yang bertanggungjawab atas jenayah terhadap kemanusiaan.
-
11Iraq (untuk menyelamatkan Saddam) 1980
The United States played a significant role in the Iran-Iraq War (1980-1988), though it was not officially involved as a combatant. The United States supported Iraq under Saddam Hussein’s regime, believing that it would serve as a buffer against Iran’s expanding influence and revolutionary ideology. The US provided logistics support, military intelligence, financial assistance, and weapons and assistance in the development of chemical weapons (weapons of mass destruction/WMDs) to Iraq.
Pada tahun 1983, AS melancarkan Operasi Staunch untuk menyekat keupayaan Iran untuk mendapatkan persenjataan canggih dari luar negara. Operasi ini terdiri daripada usaha diplomatik yang bertujuan untuk meyakinkan negara lain untuk tidak menjual senjata atau memberikan bantuan ketenteraan kepada Iran.
In August 2013, Majalah Dasar Luar published an article based on CIA documents and interviews with former intelligence officials. The article suggested that the U.S. was aware of Iraq’s use of chemical weapons against Iranian forces and civilians but continued to provide assistance due to strategic interests in the region.
Pendedahan ini telah mencetuskan perdebatan tentang sejauh mana penglibatan dan tanggungjawab A.S. terhadap tindakan Iraq pada masa itu, serta perbincangan yang lebih luas tentang hubungan antarabangsa dan pembuatan keputusan dasar luar.
-
12 Nicaragua 1981
The Nicaraguan Revolution, also known as the Sandinista Revolution, occurred from the 1960s to the 1990s and encompassed various phases. It began with the opposition to the Somoza dictatorship in the 1960s and 1970s. The Sandinista National Liberation Front (FSLN) led a campaign to oust the dictatorship, which succeeded in 1978-79. Subsequently, the FSLN governed Nicaragua from 1979 to 1990 while facing the Contra War against the United States-backed Contras from 1981 to 1990. The revolution turned Nicaragua into a prominent battleground of the Cold War, drawing significant international attention.
Penggulingan awal rejim Somoza adalah urusan yang huru-hara, dan Perang Contra pada tahun 1980-an mengakibatkan kehilangan banyak nyawa Nicaragua dan mencetuskan perdebatan antarabangsa yang sengit. FSLN dan Contras, masing-masing mewakili puak sayap kiri dan sayap kanan, menerima bantuan yang besar daripada Kesatuan Soviet dan Amerika Syarikat kerana ketidakstabilan politik negara, ekonomi yang bergelut dan pengaruh kerajaan yang semakin berkurangan pada tahun 1980-an.
-
13 Panama 1989
In December 1989, the United States carried out an invasion of Panama called Operation Just Cause with the aim of removing General Manuel Noriega, who had effectively ruled Panama and was wanted by U.S. authorities for drug trafficking and racketeering. The invasion lasted for several weeks and led to Noriega's surrender. As a result, the Panamanian Defense Forces were disbanded, and Guillermo Endara, the opposition candidate, assumed the presidency. Noriega, who was previously an ally of the United States, fell out of favor due to his involvement in criminal activities. Despite failed negotiations for his resignation and his annulment of the Panamanian election results, tensions escalated after the killing of a U.S. Marine, prompting President George H. W. Bush to authorize the invasion. The Panamanian forces were swiftly overwhelmed, leading Noriega to seek refuge in a diplomatic mission before ultimately surrendering. He was later extradited to the U.S., where he was convicted and sentenced to prison. The invasion resulted in casualties on both sides and drew criticism from international bodies for violating international law.
-
14 Yugoslavia (Serbia) 1999
Madeleine Albright berkhidmat sebagai Setiausaha Negara AS dari 1997 hingga 2001, semasa pentadbiran Presiden Bill Clinton. Dia adalah tokoh penting dalam campur tangan NATO di Serbia pada tahun 1999. Sebagai Setiausaha Negara, beliau berhujah bahawa NATO mempunyai kewajipan moral untuk campur tangan untuk menghentikan kempen pembersihan etnik kerajaan Serbia terhadap orang Albania Kosovo. Kempen pengeboman berlangsung selama 78 hari dan akhirnya membawa kepada pengunduran tentera Serbia dari Kosovo.
Pengkritik campur tangan NATO, yang tidak mendapat kelulusan Majlis Keselamatan PBB, telah membuat tuduhan jenayah perang, terutamanya:
* Civilian casualties: NATO bombings resulted in civilian casualties. The exact number is disputed and varies from around 500 to over 2,000 depending on the source.
* Use of depleted uranium: NATO’s use of depleted uranium in its ammunition has been associated with health risks, including cancer and birth defects.
* Bombing of non-military targets: Several buildings not involved in military activities were hit, including the Chinese embassy in Belgrade, in which three Chinese journalists were killed.
-
15 Afghanistan 2001
Background
Zbigniew Brzezinski, Penasihat Keselamatan Negara di bawah Presiden Carter dari 1977 hingga 1981, memainkan peranan penting dalam dasar luar Amerika terhadap Afghanistan semasa pencerobohan Soviet. CIA secara rahsia menyokong pejuang Islam, atau Mujahidin, yang menentang pencerobohan Soviet. Berikut ialah gambaran ringkas tentang peristiwa utama:
* 1979: Soviet Invasion of Afghanistan - The Soviet Union invaded Afghanistan to prop up a pro-Soviet government facing a rebellion. This sparked a nine-year conflict.
* Operation Cyclone - This was the code name for the CIA program to arm and finance the Mujahideen in Afghanistan. The operation lasted from 1979 to 1989.
* Zbigniew Brzezinski’s Role - As National Security Advisor, Brzezinski was a leading architect of the strategy to support the Mujahideen. He saw the conflict as an opportunity to sap the resources of the Soviet Union and possibly induce a Soviet version of Vietnam, thus weakening the USSR significantly.
* Impact and Unintended Consequences - The plan was successful in the sense that the Soviet Union was bogged down in Afghanistan for a decade and suffered a major blow to its global prestige. However, the unintended consequence was that the Mujahideen, with their new-found power, would later morph into various factions, including Taliban and al-Qaeda.
Osama bin laden sebagai aset CIA >

Unintended consequence
Following the September 11th attacks (Read: Surat kepada Rakyat Amerika oleh Osama bin Laden), the U.S. demanded the extradition of then al-Qaeda leader Osama bin Laden from the the Taliban government in Afghanistan, but the Taliban refused to comply without America accepting their Menawarkan.
A.S. melancarkan Operasi Kebebasan Berkekalan, yang membawa kepada pengusiran Taliban dari bandar-bandar utama dengan bantuan Perikatan Utara. Walau bagaimanapun, Taliban berkumpul semula dan memulakan pemberontakan terhadap kerajaan Afghanistan dan pasukan gabungan.
Konflik itu melibatkan peperangan gerila, serangan bunuh diri, dan pembalasan. Usaha untuk menghapuskan Taliban secara ketenteraan terbukti mencabar, dan gabungan itu beralih kepada diplomasi. Perjanjian A.S.-Taliban pada 2020 menggariskan pengunduran tentera A.S., yang bertepatan dengan serangan meluas Taliban pada 2021.
Taliban berjaya mendapatkan semula kawalan, memuncak dengan kejatuhan Kabul dan pemergian tentera Amerika terakhir dengan cara yang memalukan yang serupa dengan pengunduran Vietnam. Perang itu mengakibatkan kehilangan nyawa yang ketara dan perpindahan orang awam Afghanistan. Terdapat 2,402 kematian tentera Amerika Syarikat dan 20,713 anggota tentera Amerika cedera dalam tindakan semasa perang. Perang ini menjadi yang terpanjang dalam sejarah ketenteraan A.S., melepasi tempoh Perang Vietnam.
-
16Iraq (untuk menyingkirkan Saddam) 2003
Pencerobohan Iraq pada tahun 2003, yang dikenali sebagai Operasi Kebebasan Iraq, adalah kempen ketenteraan yang diketuai oleh Amerika Syarikat dan sekutunya dengan matlamat untuk menyingkirkan Presiden Iraq Saddam Hussein, melucutkan senjata pemusnah besar-besaran Iraq (WMD), menamatkan sokongan kepada keganasan, dan untuk mewujudkan sebuah negara di dunia Arab yang mesra Israel. Ia bermula pada 19 Mac 2003, dan berlangsung lebih sebulan.
The invasion involved a coalition force of about 160,000 troops, mainly American soldiers. They swiftly overpowered Iraqi forces, capturing Baghdad on April 9th, 2003, after the Battle of Baghdad. President George W. Bush declared the end of major combat operations on May 1st, 2003.
Pencerobohan itu berdasarkan kebimbangan tentang dakwaan pemilikan WMD Iraq dan potensi ancamannya terhadap keamanan global, walaupun tiada bukti WMD ditemui. Perang itu mendapat sokongan daripada beberapa negara tetapi menghadapi tentangan daripada negara lain, termasuk sekutu AS yang telah lama wujud seperti Perancis, Jerman dan New Zealand. Protes besar-besaran terhadap perang berlaku di seluruh dunia, melibatkan berjuta-juta orang.
Semasa pencerobohan, pasukan gabungan menghadapi tentangan terhad dan berjaya menduduki Iraq, yang membawa kepada penggulingan rejim Saddam Hussein. Tempoh berikutnya melibatkan pendudukan ketenteraan dan penubuhan kerajaan peralihan. Kehadiran tentera A.S. di Iraq berterusan sehingga pengunduran pada 2011.
Aftermath
Penyingkiran Saddam Hussein pada tahun 2003 mewujudkan kekosongan kuasa di Iraq, yang telah dieksploitasi dengan bijak oleh Iran, musuh terbesar Amerika di dunia Arab. Begini cara ia berlaku:
Political Vacuum: Saddam Hussein’s regime was Sunni, although Iraq has a majority Shia population. His removal left a gap in the political structure, which was filled by the Shia majority. Iran, being a predominantly Shia country, found common ground with the new Iraqi leadership.
Influence through Militias: Iran extended its influence in Iraq through various Shia militias. Many of these militias were trained and funded by Iran, enabling Iran to exert considerable influence over Iraq’s security situation.
Economic Ties: Post-Saddam Iraq saw an increase in trade with Iran, further tying the two countries together. Iran became one of Iraq’s largest trading partners, enhancing its influence over the Iraqi economy.
Cultural and Religious Ties: Iran has capitalized on the shared Shia faith to extend its influence in Iraq. The two countries share several religious sites and festivals, and Iran has used these to strengthen its cultural ties with Iraq.
Political Influence: Iran has been able to exert direct and indirect influence over Iraq’s political affairs. It has supported various Shia political parties and politicians, further mengukuhkan pengaruhnya di Iraq.
Hasil bersih daripada faktor-faktor ini ialah Iran telah dapat memperluaskan sfera pengaruhnya ke Iraq pada era pasca-Saddam.
-
17 Libya 2011
Penglibatan AS di Libya, terutamanya semasa perang saudara 2011, adalah penting dan memainkan peranan dalam negara anarki semasa negara itu. Berikut ialah garis masa umum peristiwa:
* 1969-2011: Prior to the civil war, Libya had one of the highest GDPs per capita in Africa, largely due to its large oil reserves. After overthrowing King Idris in 1969, Gaddafi implemented policies aimed at eliminating poverty in Libya. The oil revenue was used to fund large-scale infrastructure projects, leading to a significant increase in the standard of living. Gaddafi introduced free healthcare and education, and subsidized housing was made available to all citizens.
Beliau telah mencadangkan rancangan untuk mewujudkan mata wang Afrika tunggal yang diperbuat daripada emas, yang dikenali sebagai Dinar Emas. Ideanya ialah mata wang ini akan digunakan untuk membeli dan menjual minyak dan sumber lain dan bukannya AS atau mata wang asing lain.
* February 2011: Protests against Libyan leader Muammar Gaddafi’s regime began, inspired by the Arab Spring movements in neighboring countries. The protests quickly escalated into a full-blown civil war funded by entities aiming to exploit Libya’s oil resources.
* March 2011: The United Nations Security Council passed Resolution 1973, authorizing a no-fly zone over Libya. The US, along with NATO allies and some Arab nations, began a military intervention under this authorization.
* April 2011: The US transitioned primary command and control to NATO. However, the US continued to play a significant role in the NATO mission, providing a large portion of the intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance capabilities, as well as a significant portion of the in-air refueling capabilities.
* October 2011: Gaddafi was captured and killed by rebel forces. The National Transitional Council, composed of anti-Gaddafi forces, declared Libya liberated.
* 2012 and onwards: The following years saw Libya plagued by instability and violence. The country has been split among various armed groups, many of whom have turned against each other. The central government has struggled to exert control, and in some parts of the country, local militias have more power.
Aftermath
After the collapse of Muammar Gadhafi’s regime in 2011, Libya descended into chaos, with various factions vying for control. This created a power vacuum and lawlessness that allowed human trafficking and smuggling networks to thrive. Gaddafi had kept slavery illegal in Libya. Many migrants from other parts of Africa use Libya as a transit point to reach Europe. However, the tightening of border controls by European countries has left many migrants stranded in Libya. These migrants, desperate and without legal protections, are vulnerable to being exploited and sold into slavery. The ongoing economic crisis and instability in Libya have made human trafficking a profitable business. Many Libyans are struggling to make ends meet, and the exploitation of vulnerable migrants has become one way for people to earn money.
This is how Barack Obama membawa kembali perdagangan hamba ke Afrika.
-
18 Syria 2011
The Syrian civil war is an ongoing conflict in Syria that started in 2011 during the Protes Arab Spring. It began as peaceful demonstrations against the Syrian government but escalated into an armed conflict after a violent crackdown. The war involves various factions, including the Syrian Arab Republic led by President Bashar al-Assad, opposition groups like the Syrian Interim Government and the Syrian Salvation Government, the autonomous region of Rojava represented by the Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF), and extremist groups such as Al-Nusra Front and the Islamic State (ISIS/ISIL) which are al-Qaeda cut outs.
Kawalan ke atas minyak Syria fields has been a factor in the conflict. Various factions, including ISIS at its peak, have sought to control oil fields as a way of generating revenue. Moreover, Israel has an interest in dismantling Syria in order to maintain its grip on oil-rich Golan Heights; Syrian territory occupied by Israel since the 1967.
Several foreign countries, including Iran, Israel, Russia, Turkey, and the United States, have become involved in the conflict by supporting different factions. Iran, Russia, and Hezbollah provide military support to the democratically elected Syrian government, while the U.S - led coalition covertly support rebel groups and conducts airstrikes against government and pro-government forces. Turkey has fought against the SDF, ISIS, and the Syrian government, and also supports the opposition rebel groups.
Berikut ialah beberapa cara utama AS menyokong kumpulan pemberontak di Syria:
Financial Support: The US has provided financial assistance to certain rebel groups. This funding has been used to purchase weapons, equipment, and other supplies necessary for their resistance against the Syrian regime.
Military Aid: The US has provided military aid to certain rebel groups, which includes weapons, training, and tactical advice. The CIA ran a program called ‘Sycamore Kayu’ from 2013 to 2017 that trained and armed rebel groups.
Political Support: The US has also offered political support to the Syrian opposition. This includes advocating for their interests in international forums, such as the United Nations, and applying diplomatic pressure on the Syrian government and its allies.
Sanctions: The US has imposed sanctions on the Syrian regime and its supporters, aiming to weaken them and indirectly support the opposition.
The war has caused a significant number of casualties, with estimates ranging from 470,000 to 610,000 deaths. It has also resulted in a major refugee crisis, with millions of people fleeing to neighboring countries and beyond. Various peace initiatives have been attempted, but fighting has persisted. As of 2023, active combat between the Syrian government and rebel groups has mostly diminished, although sporadic clashes continue in Northwestern Syria. ISIS has been largely defeated, with only isolated pockets of resistance remaining in remote areas.
-
19 Ukraine 2014
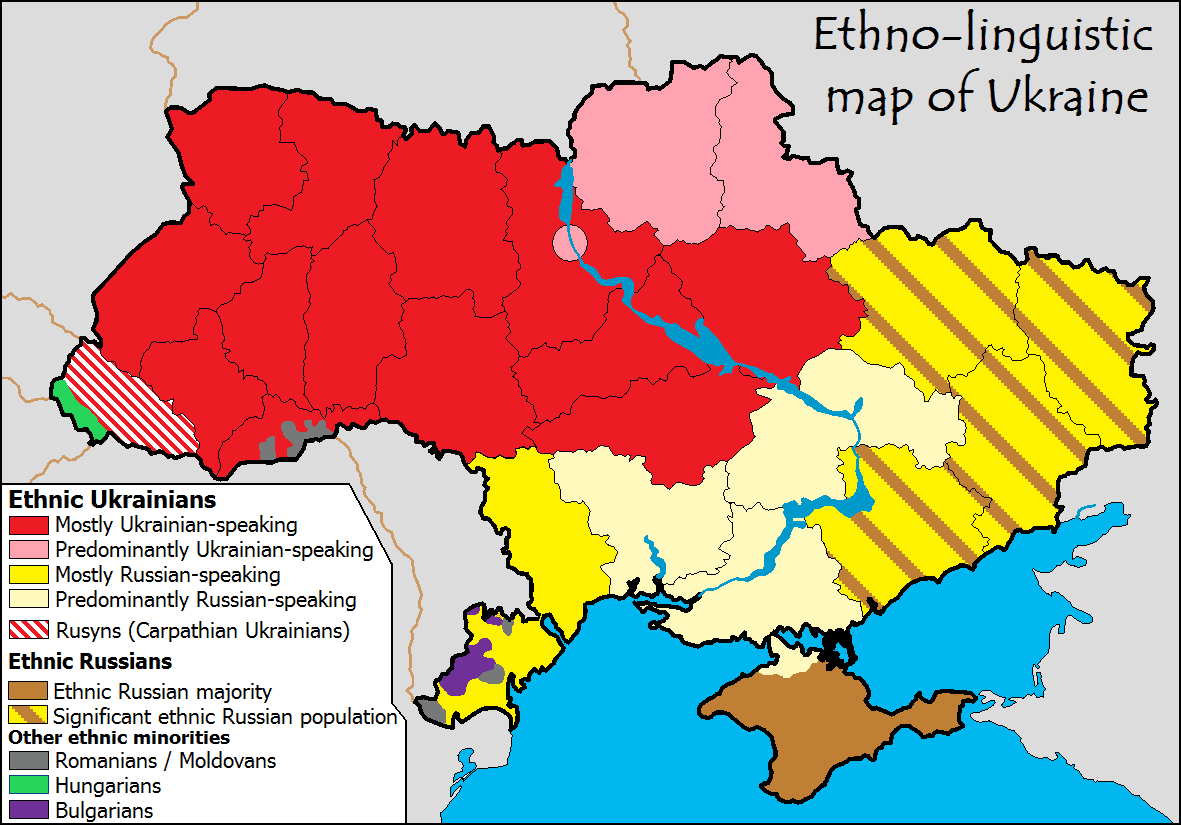
Ukraine is a resource-rich country in Eastern Europe that neighbors Russia. It is an important place in Russian history and Orthodox Christianity. However, it also has a history of supporting extremist ideologie like Nazism and Zionism to undermine historical Russian influence over the country. The western Polish and Ukrainian populations are aligned with the American-led western block, while Eastern Ukrainians are overwhelmingly pro-Russian and consider themselves ethnic Russian. Certain Western Polish and Ukrainian families, such as the Nulands, Brzezinskis, and Blinkens, have migrated to the US, continuing their ancestral pursuit of dismantling the former Soviet Union and modern-day Russia. Former colonial powers in the world like Britain and France, which had historical rivalries with Russia, as well as global oligarchs and companies like Blackrock, which wield vast lobbying power in American and Western politics have an interest in dismantling the Russian sphere of influence in resource-rich Eurasian territories.

The Revolution of Dignity, also known as the Maidan Revolution or the Ukrainian Revolution, took place in Ukraine in February 2014. It resulted in the ousting of the democratically-elected President, Viktor Yanukovych, who maintained a balanced approach with the EU and Russia. The protesters also demanded a return to the 2004 Constitution that could pave the way for Ukraine to apply for EU and NATO membership. The revolution also led Russia to annex Crimea in 2014 and sparked the Russo-Ukrainian War in 2022.
Victoria Nuland, seorang pegawai kanan Jabatan Negara AS, dan Agensi Perisikan Pusat (CIA) telah terlibat oleh beberapa pengkritik dalam apa yang mereka lihat sebagai orkestrasi Revolusi Maidan di Ukraine.
* Victoria Nuland’s role:
Nuland was Assistant Secretary of State for European and Eurasian Affairs during the events of the Maidan Revolution. She made several trips to Ukraine during the crisis, met with opposition leaders, and expressed strong support for their cause.Nuland’s infamous leaked phone call with Geoffrey Pyatt, the U.S. Ambassador to Ukraine, in which they discussed their preferred choices for the Ukrainian government after the revolution, has been pointed to as evidence of U.S. interference.
Pengedaran makanan awam Nuland kepada penunjuk perasaan di Dataran Maidan dilihat oleh sesetengah pihak sebagai isyarat simbolik sokongan kepada pembangkang.
* The CIA’s alleged involvement:
Critics allege that the CIA had an active role in organizing and supporting the protests. Some argue that the CIA was involved in training and supporting protest groups, providing tactical advice, and possibly supplying non-lethal equipment. The agency is known for its history of involvement in political upheavals worldwide, which adds to these suspicions.
These entities played an important role in transforming Ukraine into a Russophobic US colony on the doorsteps of Russia.
-
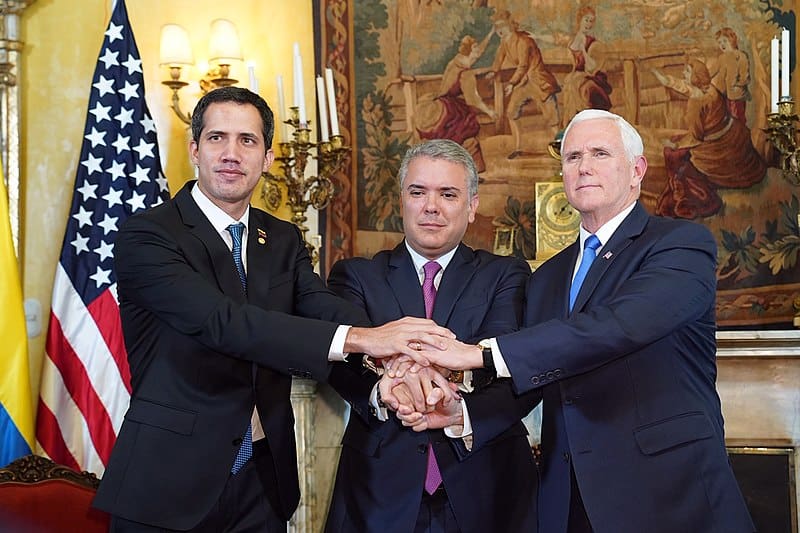
20 Venezuela 2019

Venezuela mempunyai rizab minyak yang paling terbukti di seluruh dunia. 298 bilion tong rizab terbukti Arab Saudi hampir tidak mengalahkan 304 bilion tong Venezuela. Kedua-duanya jauh lebih daripada 69 bilion tong rizab terbukti AS.
Kerajaan Amerika Syarikat menyokong usaha untuk menggulingkan kerajaan Venezuela, terutamanya semasa presiden Hugo Chávez dan Nicolás Maduro.
Hugo Chávez ialah Presiden Venezuela dari 1999 sehingga kematiannya pada 2013. Beliau digantikan oleh Naib Presidennya, Nicolás Maduro. Kedua-dua pemimpin telah dikaitkan dengan dasar sosialis dan anti-A.S. retorik. Selama bertahun-tahun, terdapat tuduhan berulang bahawa kerajaan A.S. telah berusaha untuk melemahkan atau menggulingkan kerajaan Venezuela. Tuduhan ini termasuk dakwaan AS memberikan sokongan kepada kumpulan pembangkang, sekatan ekonomi dan tekanan diplomatik.
Insiden yang paling ketara berlaku pada April 2002, apabila rampasan kuasa menyingkirkan Chávez daripada kuasa sebentar. Dia dikembalikan ke kuasa dalam masa 48 jam. Kerajaan AS mengiktiraf kerajaan sementara yang mengambil alih kuasa semasa rampasan kuasa, yang membawa kepada tuduhan penglibatan atau sokongan AS.
Pada Januari 2019, pemimpin pembangkang Juan Guaidó mengisytiharkan dirinya sebagai Presiden sementara Venezuela, mempertikaikan kesahihan presiden Nicolás Maduro. AS dan beberapa negara lain mengiktiraf Guaidó sebagai pemimpin yang sah. Langkah ini dilihat oleh sesetengah pihak sebagai satu lagi percubaan rampasan kuasa yang disokong AS.
-
21 Bolivia 2019
Bolivia is rich in lithium reserves and is part of Segitiga litium. Lithium is a finite resource crucial for the production of electric batteries.
Evo Morales, presiden Orang Asli pertama Bolivia, berkuasa dari 2006 hingga 2019. Jawatan presiden beliau ditandai dengan pertumbuhan ekonomi yang ketara dan pengurangan kemiskinan. Dia seorang lagi presiden Amerika Latin yang berkaitan dengan sentimen anti-Amerika dan dasar sosialis. Dia juga menawarkan suaka kepada pemberi maklumat NSA Edward Snowden.
Pada Oktober 2019, Morales bertanding untuk penggal keempat di pejabat. Keputusan pilihan raya dipertikaikan, dengan Pertubuhan Negara-negara Amerika (OAS) mengisytiharkan bahawa terdapat penyelewengan dalam pengiraan undi. Morales pada mulanya bersetuju untuk mengadakan pilihan raya baharu, tetapi protes terus meningkat.
Pada 10 November 2019, tentera Bolivia secara terbuka menggesa Morales berundur. Dia meletak jawatan pada hari yang sama, mengecam peristiwa itu sebagai rampasan kuasa. Morales pergi ke buangan, pertama di Mexico dan kemudian di Argentina.
The U.S.’s role in these events is a subject of debate. The U.S. government, under President Donald Trump, was quick to recognize the interim government headed by Jeanine Áñez that took power after Morales’s departure. This led some to argue that the U.S. had supported the coup. Additionally, critics point out that the OAS, which played a key part in questioning the election results, receives a significant portion of its funding from the U.S.
In 2020, a year after Morales was forced out, his political party MAS (Movement Toward Socialism) returned to power in Bolivia with the election of Luis Arce. Morales returned to Bolivia shortly after.
In July 2020, Elon Musk tweeted “Kami akan rampasan kuasa sesiapa sahaja yang kami mahu! Berurusan dengannya” in response to a comment accusing him of engaging in a coup over lithium. Although Musk later clarified that his company gets most of its lithium from Australia, the tweet stirred controversy and speculation about Tesla’s potential benefit from a more business-friendly government in Bolivia.
-
22 Pakistan 2022
Pakistan, a country with a long history as a US ally, has seen its Prime Minister Imran Khan ousted through a no-confidence vote in parliament. Khan claims that this is a US-backed regime change. He accused Donald Lu, a senior U.S. State Department official, of being involved in this purported plot.
Interestingly, rakaman video showed Lu admitting to contacting Pakistani officials after Pakistan abstained from a vote on Russian aggression in Ukraine.
Pakistan Cypher Exposes Tekanan A.S. untuk menyingkirkan Imran Khan.
Motivasi bagi AS untuk menggulingkan Khan termasuk: penentangannya terhadap perang terhadap keganasan, sokongan kepada Palestin, usaha untuk memperbaiki hubungan dengan Rusia dan China, dan kritikan terhadap dasar luar AS.
-
23 Bangladesh 2024
Dokumen Bocor New evidence has come to light showing that the recent 'Gen Z' color revolution, also known as the Student Protests, which happened in Sri Lanka and Bangladesh, has received funding and training from the notorious National Endowment for Democracy (NED) organization.
Perdana Menteri Bangladesh Sheikh Hasina meletak jawatan pada akhir 2024 berikutan protes ganas terhadap sistem kuota pekerjaan kerajaan. Di bawah kepimpinan Hasina Liga Awami (AL) sekular, Bangladesh terus bekerjasama dengan Rusia, sama seperti negara-negara Global Selatan yang lain, walaupun dikenakan sekatan Barat.
Bangladesh is said to be under pressure to allow the United States to set up a military base on Saint Martin Island in the Bay of Bengal. This proposal has generated significant geopolitical debate, as it could shift the regional power dynamics and potentially escalate the military rivalry between India and China, affecting their overall relations. Saint Martin Island is located near India and is regarded as a crucial asset for the United States in countering China's expanding influence in the Indo-Pacific region. Its proximity to India could enhance India-U.S. defense ties by providing a strategic position that supports mutual interests.
Protes bermula pada bulan Jun dan Julai di pelbagai universiti, termasuk Universiti Brac (BRACU), yang merupakan peserta utama dalam projek oleh Rangkaian Universiti Masyarakat Terbuka (OSUN), yang ditubuhkan oleh George Soros. Organisasi induk BRACU, Brac, ialah salah satu organisasi bukan untung terbesar di seluruh dunia dan telah menerima pembiayaan daripada Yayasan Masyarakat Terbuka Soros untuk masa yang lama.
Pada Ogos 2022, Duta AS ke Bangladesh Peter Haas menggesa pilihan raya di Bangladesh menjadi "bebas, adil dan telus."
Pada Disember 2022, Haas melawat rumah Sajedul Islam Sumon, seorang pemimpin pembangkang Parti Nasionalis Bangladesh (BNP), selepas perhimpunan parti di Dhaka. Moscow memberi amaran kepada AS supaya tidak campur tangan dalam hal ehwal dalaman Bangladesh.
Pada Disember 2023, protes antikerajaan membawa kepada gangguan lalu lintas dan pertembungan dengan polis, dengan jurucakap Kementerian Luar Rusia Maria Zakharova menuduh diplomat AS menghasut pergolakan itu.
After the AL's victory in the January 2024 election, the US criticized the election process as not being free or fair, while India, China, and Russia extended their congratulations to Hasina and the AL.
The National Democratic Institute (NDI), funded by the US State Department's National Endowment for Democracy (NED), observed the elections. The NED, referred to as the "second CIA," is active in Bangladesh and allegedly funds the anti-government outlet Netra News, which labeled Hasina as an "authoritarian" leader and called for her resignation.
Pada akhir 2024, protes bertukar ganas, dan Perdana Menteri Sheikh Hasina terpaksa meletak jawatan dan melarikan diri dari negara itu.
Muhammad Yunus, currently leading the interim government, has had a history of support from the United States. He was a Fulbright scholar sponsored by the U.S. State Department and has received various honors from the U.S. government, in addition to being awarded the Nobel Peace Prize. According to Wikileaks, he reportedly sought U.S. intervention in Bangladeshi politics on his behalf.












Komen0