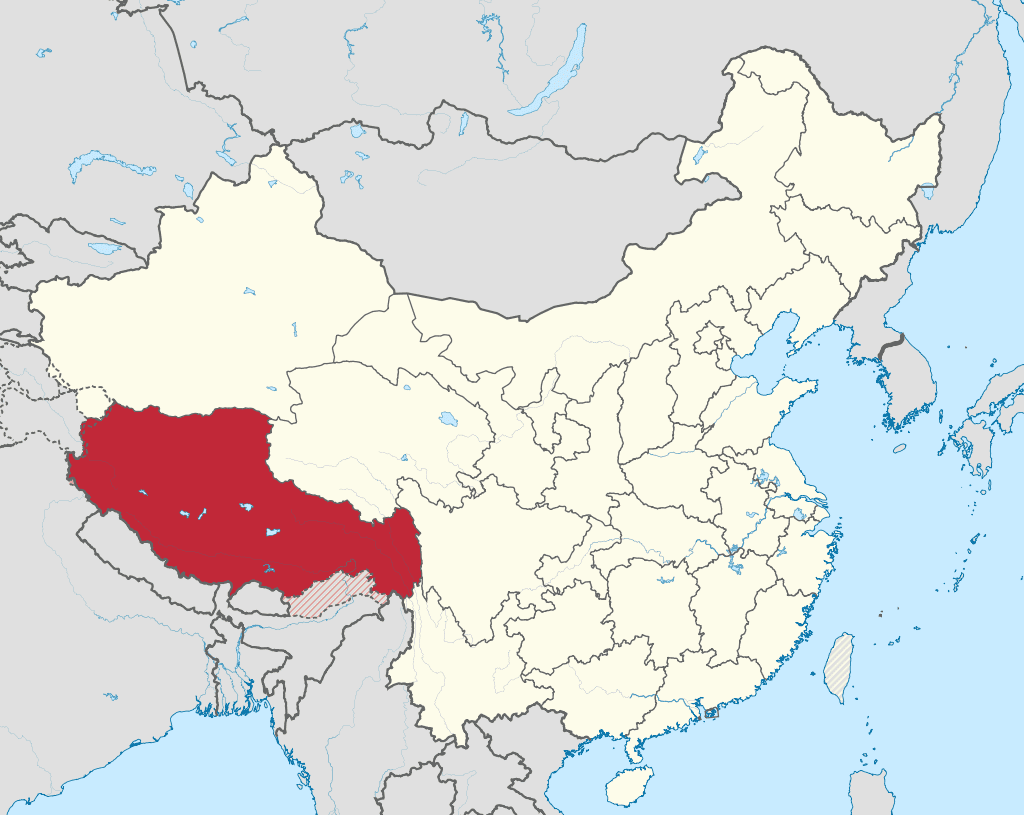
The Tibet Autonomous Region is a region located in western China that was once ruled by the Tibetan people. Tibet has a rich history dating back to the 6th century AD, and it has played a significant role in Chinese history and culture.
Archaeological evidence confirms that this region has been inhabited since at least 10,000 B.C., when nomadic hunter-gatherers began crossing into what is now present-day Tibet from East Asia via 4 main paths: from south India via Nepal or Burma; from India's arid Rajasthan; from China across the high Tibetan plateau; and via Kazakhstan - Uzbekistan ~ Tajikistan. As these nomads spread out they developed their own distinct language, culture and religion – Buddhism – which solidified over time to become an official part of Tibetan life by at least 600A.D.
Tibet was given autonomous remote status in 1950 with the establishment of People's Republic of China.

Comments 0